The intricate fabric of skin health is profoundly influenced by numerous factors, among which diet and gut health stand out as critical yet often overlooked elements. One skin condition that encapsulates the mysterious interplay between these factors is rosacea, a common dermatological challenge that affects millions worldwide. As modern research delves into the connection between our dietary habits, the microorganisms that inhabit our gut, and the expression of rosacea, we find ourselves on the cusp of a paradigm shift in the way we approach skin care and wellness. This article explores the nuanced relationship between diet, the gut microbiome, and rosacea, unraveling the complexities that confound both sufferers and scientists alike.
Understanding Rosacea
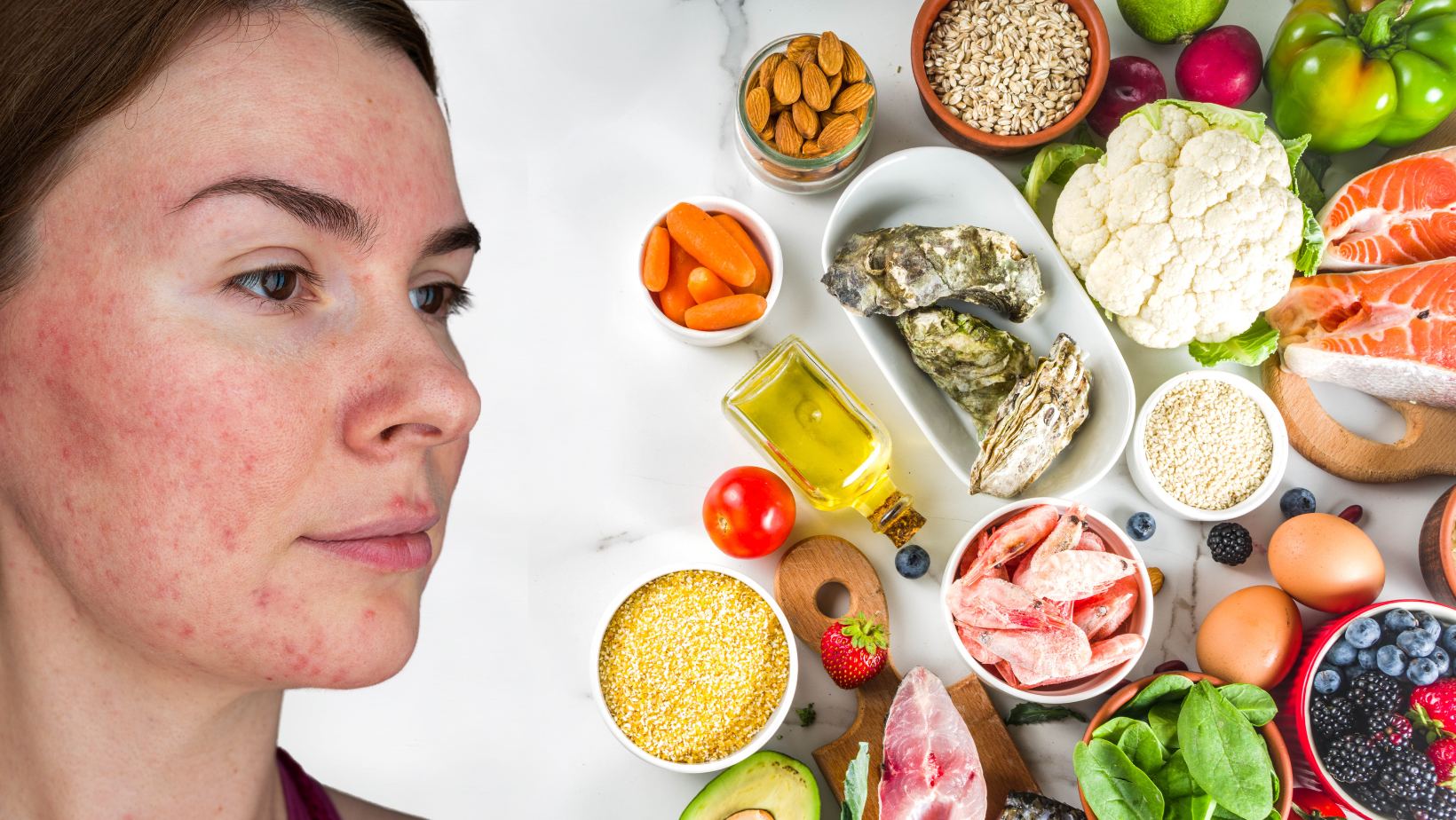
Rosacea is a perplexing skin condition marked by redness, swelling, and sometimes pimple-like bumps on the face, often accompanied by a stinging sensation and heightened skin sensitivity. While it predominantly affects fair-skinned individuals, rosacea does not discriminate entirely, casting a wider net across various ethnicities and skin types. The development of rosacea is believed to be due to a convoluted mix of genetic predispositions and environmental triggers, with the immune system playing a possible role in its pathogenesis.
Those with rosacea experience a spectrum of symptoms that can ebb and flow over time. Episodes of intense flushing and persistent redness are common, and in some cases, individuals may develop rhinophyma, a thickening of the skin on the nose that can be particularly distressing. Eye complications, known as ocular rosacea, can also arise, posing a threat to vision. Despite its prevalence, the precise causes of rosacea remain enigmatic, leaving researchers to piece together the puzzle of its true origins.
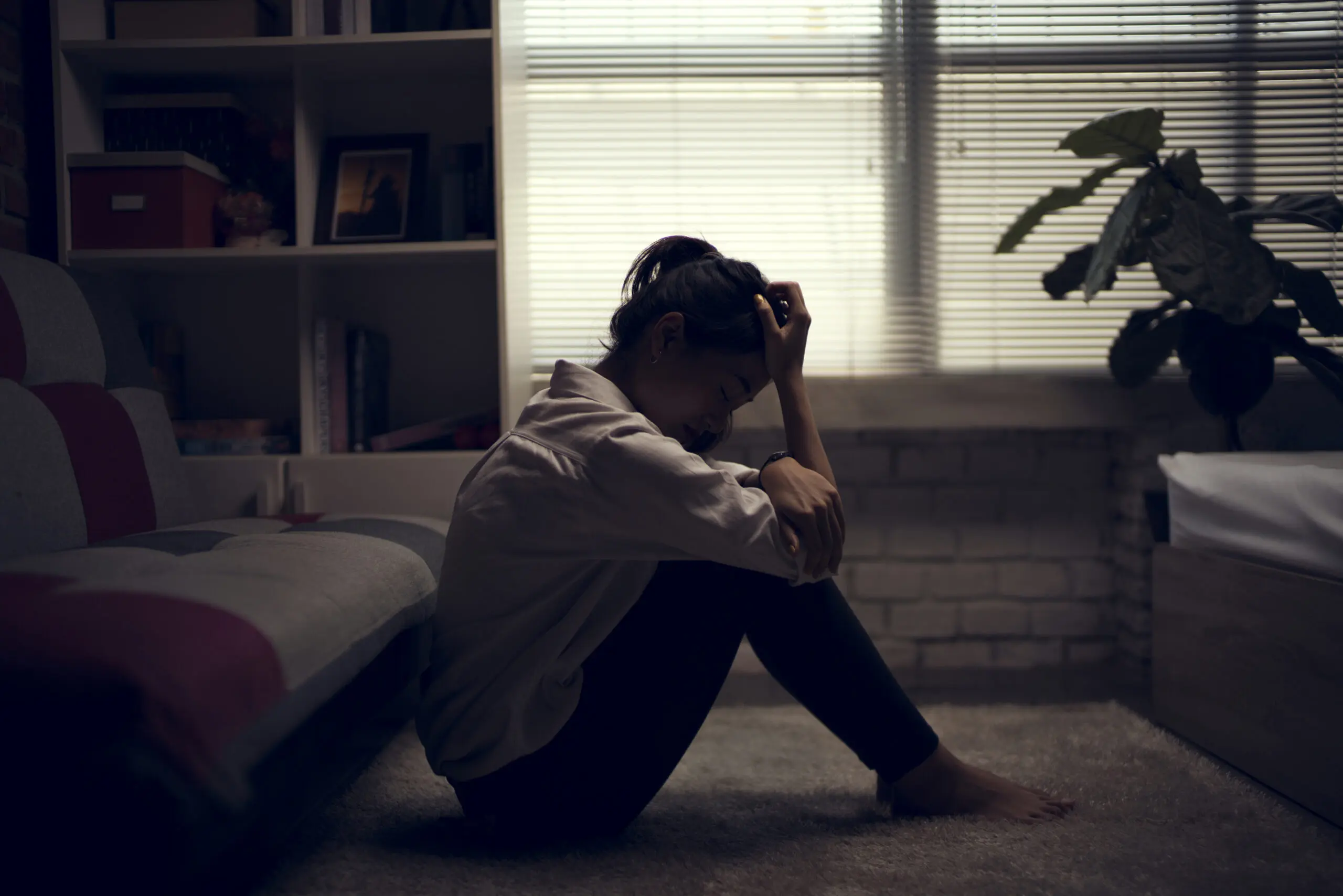
Beyond physical symptoms, rosacea often affects mental health, contributing to social anxiety, depression, and reduced quality of life. Stigma and misunderstanding can worsen these effects. If you’re located in NYC and facing emotional challenges linked to rosacea, consider How to Manage Anxiety and Depression with Anat Joseph at My Psychotherapy for professional support.
The Gut Microbiome: A Hidden Player in Rosacea
Our gut microbiome—a thriving community of bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms—exerts a significant influence on our overall health. It is integral to digestive health, immune function, and even has ties to mental well-being. Disturbances in this microbial ecosystem can lead to conditions like “leaky gut,” where the intestinal barrier becomes compromised, potentially leading to systemic inflammation and contributing to a host of disorders, including rosacea.
Emerging research points to a connection between the health of our gut and the health of our skin, conceptualized as the gut-skin axis. The presence of conditions such as small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) and inflammatory bowel diseases appear to correlate with higher instances of rosacea, suggesting a biological link that warrants further exploration.
Specific microorganisms like Helicobacter pylori, known for its role in peptic ulcers, have also been implicated in the exacerbation of rosacea symptoms. The exact mechanisms—whether they involve an immune response, inflammation, or other pathways—remain subjects of intensive scientific inquiry.
The Rosacea Diet
What we consume can have profound effects on rosacea. Certain items known for causing vasodilation and inflammation, such as alcohol, caffeine, and spicy foods, are recognized as common triggers for rosacea flare-ups. The link between these foods and rosacea symptoms is not fully understood, but it’s clear that dietary habits play a role. Modern diets, often high in sugar, fat, and processed ingredients, tend to promote inflammation, potentially worsening conditions like rosacea. In contrast, diets that emphasize anti-inflammatory foods—rich in fiber, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids—may offer some protective effects against the flare-ups characteristic of rosacea.
The individualized nature of rosacea implies that dietary recommendations must be tailored to each person. Foods that trigger a reaction in one individual may have no effect on another, highlighting the importance of a personalized approach to dietary management. This could involve allergy testing or elimination diets to identify and control personal dietary triggers.
Personalized Nutrition
The rise of personalized medicine has ushered in an era where individual genetic, microbiotic, and environmental factors can help shape dietary plans. For those with rosacea, this personalized approach offers the potential for diets that are specifically designed to avoid triggers and alleviate symptoms. Advances in genomics and biometrics have given us tools to better understand the unique factors that contribute to each person’s experience of rosacea. With these tools, healthcare providers can develop personalized nutrition plans that aim to improve skin health and mitigate rosacea symptoms.
However, personalized nutrition is not without its challenges. Implementing such a tailored approach requires cooperation among dermatologists, nutritionists, and geneticists to create comprehensive plans that are safe, balanced, and effective. The opportunities for those with rosacea, though, make the pursuit of personalized dietary interventions a compelling and potentially transformative path forward.
Practical Tips for Rosacea Management through Diet
- Keeping a Food Diary: Monitoring what you eat and how it affects your rosacea can identify potential triggers, empowering you to make informed dietary choices.
- The Elimination Diet: Gradually removing foods from your diet and then reintroducing them can help pinpoint triggers, ideally under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Incorporating Gut-Healthy Foods: A diet rich in probiotics, prebiotics, fiber, and anti-inflammatory nutrients can promote a balanced gut microbiome, possibly leading to reduced rosacea symptoms.
- Hydration and Skin Health: Proper hydration supports skin barrier function and can enhance the effectiveness of dietary management in rosacea.
- Collaborating with Healthcare Providers: Working with dieticians and dermatologists can provide valuable insights into safe and effective dietary strategies for rosacea management.
The intersection of diet, gut health, and rosacea is a field ripe with potential for developing novel treatment strategies. Personalized nutrition, tailored to the unique needs of individuals with rosacea, stands as a beacon of hope in the quest for better management of this condition. As research continues to unravel the complex web of factors that contribute to rosacea, those affected can look forward to more sophisticated, effective approaches to maintaining skin health and enhancing their overall quality of life. With the right knowledge and support, managing rosacea through diet can become an empowering and life-changing endeavor.