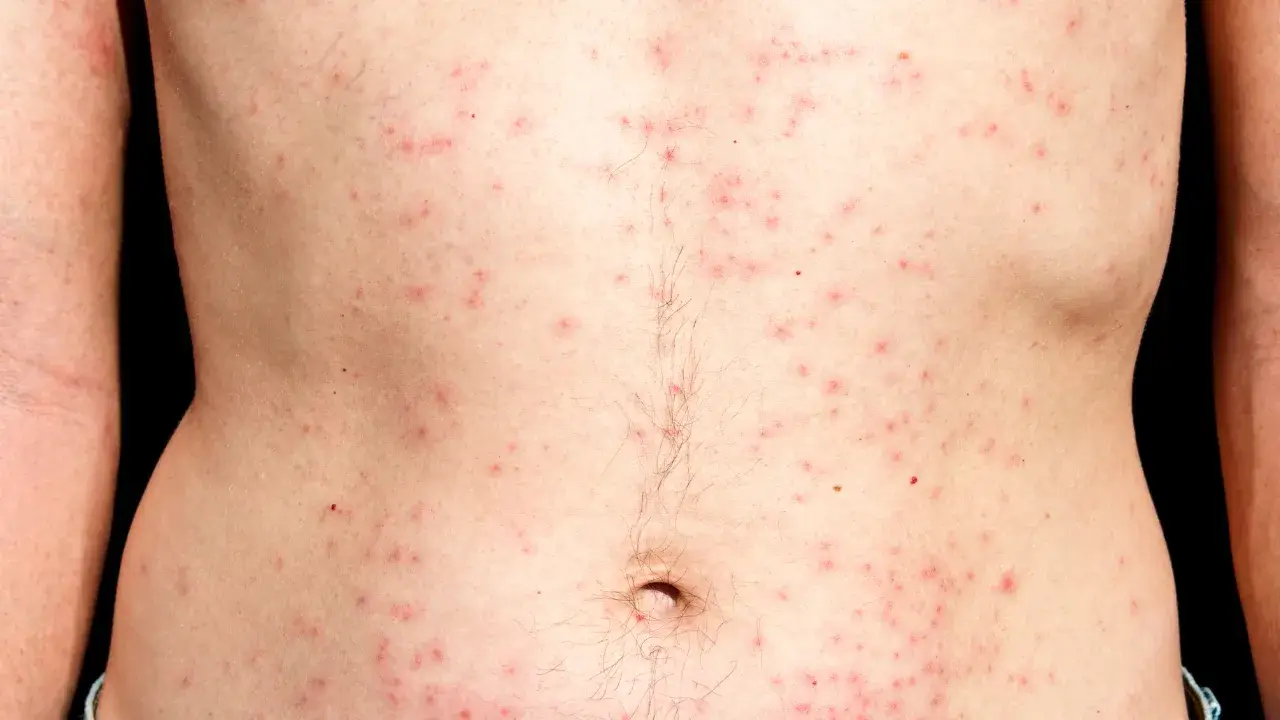
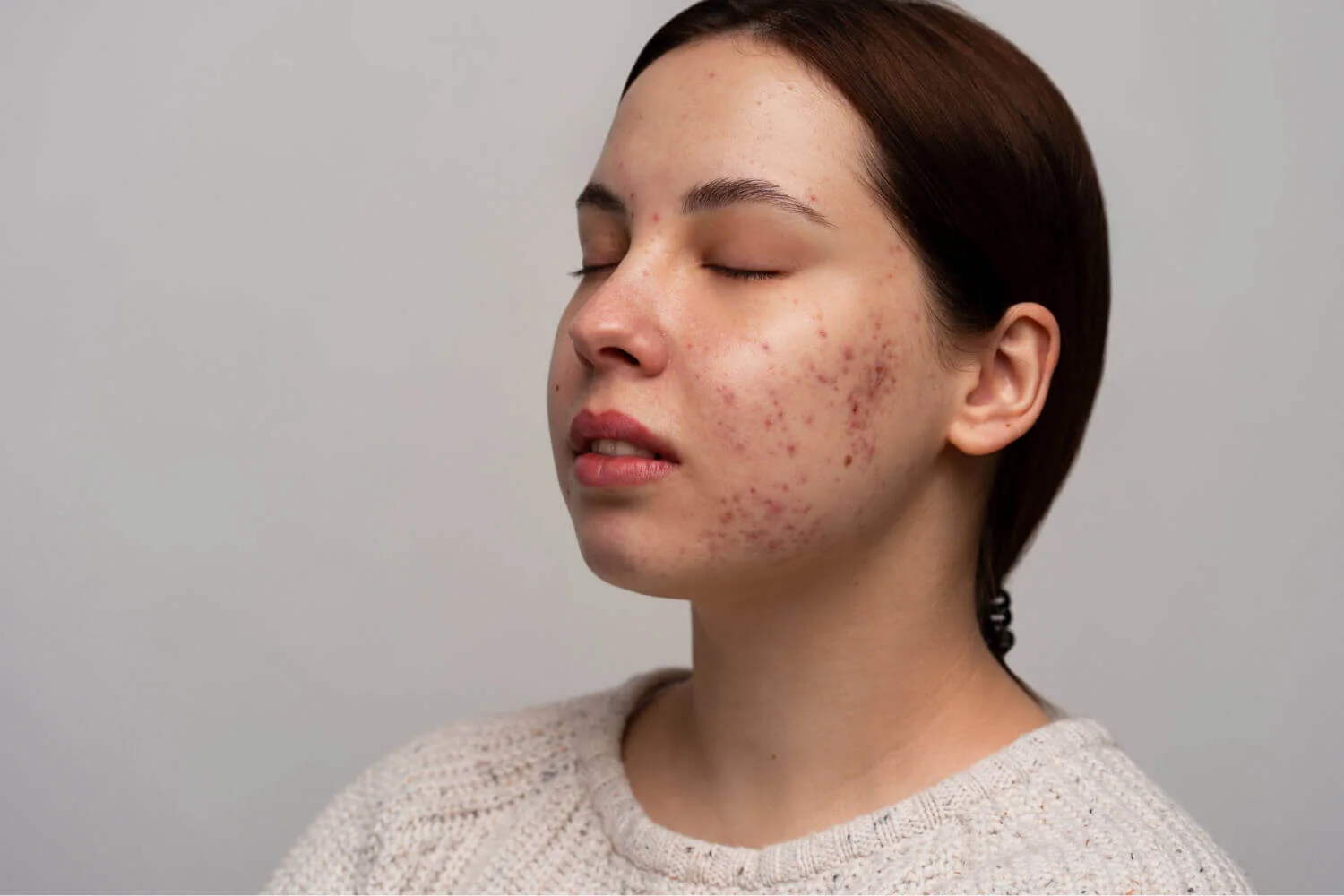
Have you ever noticed itchy, red bumps on your skin after shaving or spending time in a hot tub? You might have mistaken these bumps for acne. However, a closer look reveals that these pesky bumps could be a sign of folliculitis, a common skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become inflamed. Often caused by bacterial or fungal infections, folliculitis can result in uncomfortable and sometimes painful bumps on the skin.
Living with folliculitis can be challenging, but understanding the condition is the first step toward effective management. In this article, we will explore the ins and outs of folliculitis, from its cases and symptoms to effective treatments and prevention strategies, helping you take control of your skin health and banish these bothersome bumps.
What is Folliculitis?
Folliculitis is the inflammation of hair follicles, resulting in the appearance of red, swollen bumps on the skin. It can occur anywhere on the body where hair grows but is most common on the face, scalp, chest, back, buttocks, and legs. The condition can be acute or chronic, with chronic cases often requiring more intensive treatment. While mild cases of folliculitis often resolve on their own, more severe or persistent cases may require topical or oral antibiotics or antifungal medications. Factors such as shaving, tight clothing, hot tub use and excessive sweating can increase the risk of developing these bumps. Proper hygiene, avoiding irritants and using clean razors are just a few precautions among many to take to prevent this uncomfortable condition.
Folliculitis vs. Acne
Folliculitis and acne are both inflammatory skin conditions that share the common thread of affecting hair follicles, yet they each have distinct factors and characteristics. Acne is primarily associated with the blockage of hair follicles due to an accumulation of oils, dead skin cells, and bacteria, leading to the formation of comedones, papules, and pustules. It’s intricately linked with hormonal changes and typically manifests on the face, chest, and back. Folliculitis, on the other hand, results from an infection or irritation of the hair follicles, often by bacteria or fungi, and can arise on any part of the body where hair is present. Unlike acne, which can be chronic and often appears during adolescence, folliculitis can be an acute condition, triggered by factors like shaving, friction from clothing, or immersion in a contaminated hot tub. While both conditions can produce red, inflamed bumps on the skin, folliculitis bumps are more likely to be itchy and resemble a rash. Nonetheless, both can cause psychological distress and benefit from a tailored skincare and treatment regimen. Understanding the distinguishing elements of these conditions is crucial in devising effective treatment strategies and proper patient education for management of their symptoms.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Folliculitis
- Red Bumps: Small, red, pus-filled bumps around hair follicles.
- Itching: Affected areas may be itchy and uncomfortable.
- Pain: Some bumps can be painful or tender to the touch.
- Crusting: Pustules can break open, leading to crusting or scabbing.
- Swelling: Inflammation can cause the surrounding skin to swell.
Causes of Folliculitis
Understanding the causes of folliculitis involves looking at a range of different factors that contribute to the condition. Infectious agents, such as the ubiquitous bacterium Staphylococcus aureus and various types of fungi, are the primary culprits in many cases. These organisms invade and irritate the hair follicles, setting the stage for inflammation. However, the story doesn’t end with microorganisms; there are non-infectious players as well. Friction from tight clothing, excessive sweating, and injuries to the skin, including shaving or other forms of hair removal, can also damage follicles and foster inflammation. Furthermore, certain conditions, such as immunodeficiency, diabetes, and obesity, can increase the risk of developing folliculitis. These risk factors, along with environmental contributors like hot tubs and swimming pools with imbalanced chemical levels, paint a detailed picture of the various origins of folliculitis, each influencing the skin’s vulnerability in its own way.
Different Types of Folliculitis
There are several types of folliculitis, each with distinct causes and characteristics:
- Bacterial Folliculitis: The most common form, often caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
- Hot Tub Folliculitis: Caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, this type is associated with poorly maintained hot tubs.
- Pityrosporum Folliculitis: A fungal infection caused by Malassezia yeasts.
- Barber’s Itch: Folliculitis occurring in the beard area of men, typically from shaving.
- Gram-negative Folliculitis: Often a complication of long-term antibiotic treatment for acne.
Treatment Options for Folliculitis
Managing folliculitis typically involves addressing the underlying cause and alleviating symptoms:
- Topical Antibiotics: Creams or ointments containing antibiotics can treat bacterial folliculitis.
- Oral Antibiotics: In severe cases, oral antibiotics may be prescribed to clear the infection.
- Antifungal Treatments: Topical or oral antifungal medications are used for fungal folliculitis.
- Antiviral Medications: For viral folliculitis, antiviral drugs may be necessary.
- Home Remedies: Warm compresses, good hygiene, and avoiding irritants can help manage symptoms. Over-the-counter treatments, such as hydrocortisone cream, can reduce inflammation and itching.
Preventing Folliculitis
Preventing folliculitis involves taking several proactive steps to protect and care for your skin. Maintaining good personal hygiene is fundamental, which includes regular showering and thoroughly drying off afterwards. It’s essential to avoid sharing personal items such as towels, razors, or clothing that come into contact with the skin. Wearing light, non-restrictive clothing can reduce friction and sweating, both of which can irritate hair follicles. For those who shave, using a sharp, clean razor and shaving in the direction of hair growth helps minimize irritation and potential nicks to the skin. If you’re prone to folliculitis, it can be beneficial to take breaks from shaving to allow your skin to recover. Properly maintaining hot tubs and pools is necessary to prevent bacterial growth that can cause folliculitis, and you should shower straight after using such facilities. Lastly, managing pre-existing skin conditions, keeping skin well-moisturized, and considering the use of antiseptic or antibacterial products when recommended by a healthcare professional are all strategies that can help keep folliculitis at bay.
Beyond the Bumps: Possible Complications
While folliculitis is generally not serious, complications can occur, especially if the condition is not treated promptly:
- Boils and Carbuncles: Untreated folliculitis can lead to deeper infections, resulting in painful boils or carbuncles that require medical intervention.
- Scarring: Chronic or severe folliculitis may cause permanent scarring or hyperpigmentation.
- Cellulitis: Infections can spread to surrounding skin, leading to cellulitis, a potentially serious condition requiring antibiotic treatment.
- Follicular Destruction: Repeated or severe folliculitis can damage hair follicles, leading to permanent hair loss in the affected area.
The Broader Impact of Folliculitis on Well-being and Lifestyle
The impact of folliculitis stretches beyond the visible bumps and skin irritation. The constant concern over the appearance of skin lesions can lead to a decrease in self-confidence, reluctance in social situations, and even significant stress that exacerbates the condition itself. Additionally, the persistent nature of folliculitis can mean a long-term commitment to treatment regimens, which may be both time-consuming and financially burdensome. Moreover, the physical discomfort associated with folliculitis, such as itching and pain, can be a hindrance to regular activities and can decrease the overall quality of life. Understanding and addressing these multifaceted effects are key in providing a holistic approach to patient care. By creating a supportive environment, offering resources for emotional support, and facilitating access to effective medical treatments, healthcare providers can help individuals navigate the challenges wrought by folliculitis. This comprehensive perspective ensures that the fight against folliculitis is not just about clearing the skin, but also about nurturing the individual’s overall health and happiness.
Future of Folliculitis Management
Continued research into folliculitis is essential for developing a deeper understanding of the condition and improving treatment options. Future research directions include microbiome studies aimed at altering skin flora for the prevention and treatment of folliculitis, exploring genetic predispositions to tailor personalized therapies, and investigating novel pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions resistant to microbial resistance.
There is also a need to understand the inflammatory mechanisms and immune responses involved in folliculitis to discover new anti-inflammatory treatments. Preventive strategies and educational programs, especially for those at higher risk, are valuable for managing the condition. Furthermore, assessing the psychosocial impact of folliculitis will inform the development of comprehensive care resources supporting mental health and quality of life.
Lastly, researching the skin’s barrier function could lead to advancements in barrier-enhancing treatments. Engaging with medical research communities, attending relevant conferences, and staying informed on the latest literature will allow for continuous learning and contribute to future discoveries in managing folliculitis.
Folliculitis is a common but manageable skin condition. By maintaining sound skincare practices and staying informed about emerging treatments, those affected can effectively navigate the challenges posed by this condition.
Continuously emerging research and the integration of new findings into clinical practice will pave the way for more personalized, effective management strategies. With each new discovery and new insight, we are working towards building a stranger foundation for future breakthroughs that could one day transform the landscape of folliculitis care. It is through this persistent endeavor that we can hope to unlock more sophisticated diagnostic tools and treatment and ultimately uplift the well-being of individuals grappling with this condition, to create a future where managing folliculitis is more accessible and less distressing.