Far more than a simple skin condition, Hidradenitis Supparativa weaves a path of chronic inflammation and pain through the lives of those it touches, profoundly influencing their daily well-being. Characterized by throbbing, angry bumps in some of the most sensitive areas of the body including the armpits, groin, and under the breasts, these painful lesions make every movement excruciating and remind you of their presence with every brush against clothing or skin. For those living with Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS), this reality is an everyday battle.
HS is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that deserves much more attention and awareness. Beyond just the physical pain of these recurring bumps in friction-prone areas, HS can take an immense emotional toll. The self-consciousness and mental strain of having to constantly manage this condition adds an extra heavy burden.
If these struggles sound all too familiar, you’re not alone. Whether you are dealing with HS yourself, supporting a loved one, or simply looking to learn more, this article will explore HS in detail, breaking down its symptoms, stages, the various factors that contribute to its development, and treatment. By understanding HS, its causes, symptoms and how to best treat and cope with it, you can regain some control over this debilitating condition.
What is Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
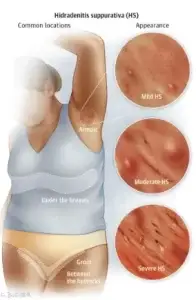
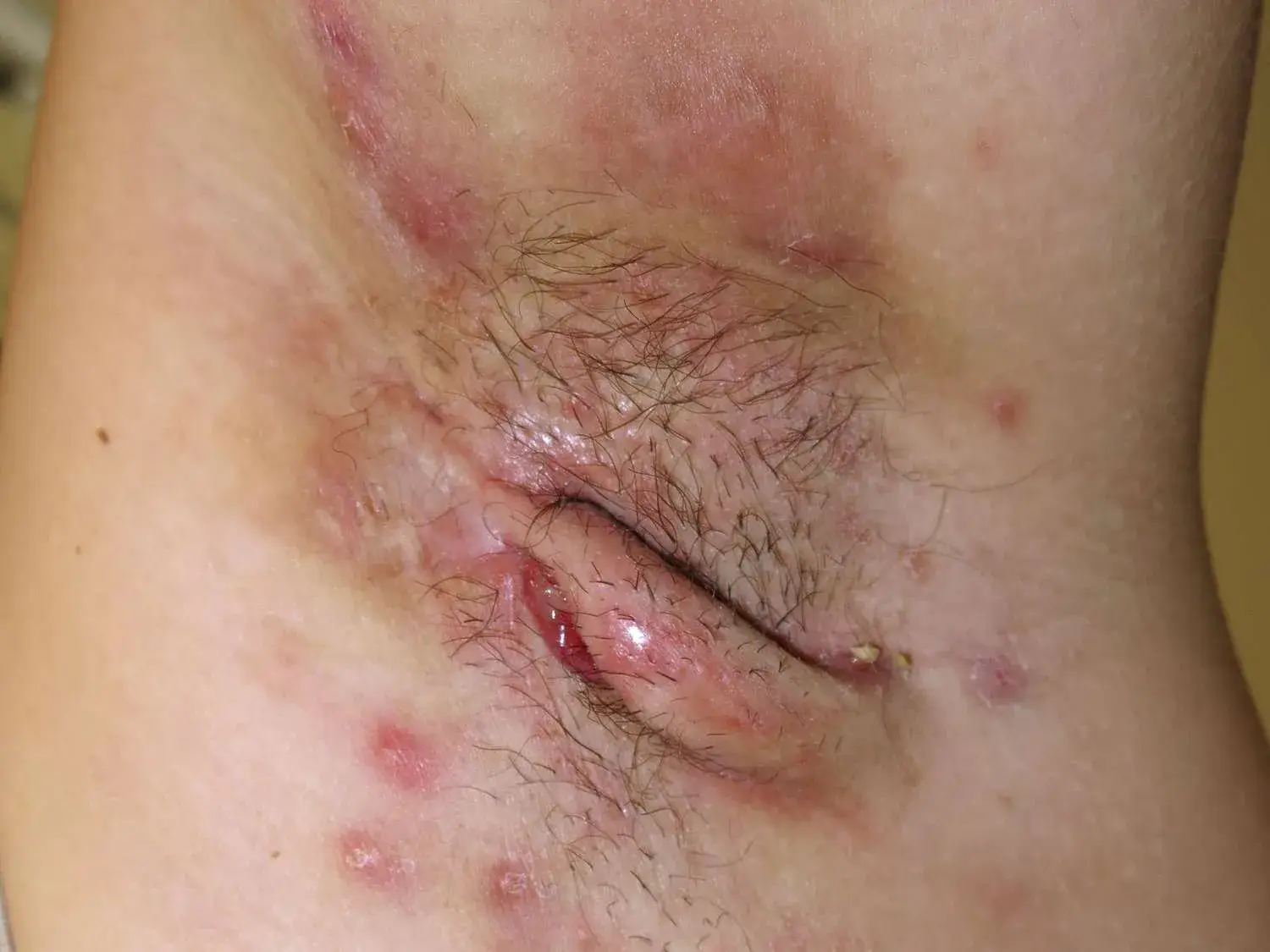
Hidradenitis Suppurativa is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that causes small, painful lumps under the skin. These lumps can break open, causing abscesses that may drain pus and blood, leading to significant discomfort and potential scarring. HS typically occurs in areas where skin rubs together, such as the armpits, groin, buttocks, and under the breasts. HS can persist for many years, with periods of flare-ups and remission. The exact cause of HS is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, hormonal and environmental factors. For this reason, early diagnosis and treatment is essential to managing symptoms and preventing complications.
How Common is Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
The prevalence of Hidradenitis Suppurativa varies across the globe. However, the estimated global prevalence ranges from 0.00033% to 4.1%. In developed countries, like Europe and the US, the prevalence is relatively higher, ranging from 0.7% to 1.2%. Unfortunately, data on the prevalence of HS in developing countries is limited and further research is required to assess the burden of the disease in these regions.
What Causes Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
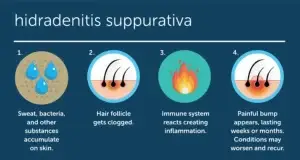
The exact cause of HS is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to inflammation and blockage of hair follicles. Factors that may contribute to HS include:
Genetics:
Genetics play a crucial role in the development of HS. Studies have shown that a family history of HS significantly increases the risk of developing the condition. This suggests that certain genetic mutations may predispose individuals to hair follicle blockage and inflammation. If someone in your immediate family has HS, your chances of developing it are considerably higher. This hereditary aspect highlights the importance of understanding family medical history in managing and anticipating HS.
Hormonal Changes:
Hormones are another significant factor in HS. The condition frequently appears or worsens during periods of hormonal fluctuation, such as puberty, menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and menopause. Androgens, which are male hormones present in both men and women, are believed to influence the condition. These hormones can impact the sebaceous (oil) glands and hair follicles, leading to the characteristic symptoms of HS. Understanding the hormonal link can help in managing flare-ups and considering treatments that address hormonal imbalances.
Immune System Irregularities:
The immune system’s role in HS is pivotal. In individuals with HS, the immune system appears to be hyperactive, leading to chronic inflammation. This overactive immune response targets hair follicles, causing them to become blocked and inflamed. Some researchers classify HS as an autoinflammatory condition, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues. This chronic inflammation is a key driver of the painful lesions and tunnels that develop in HS.
Lifestyle Factors:
Lifestyle choices significantly affect the severity and frequency of HS symptoms. Two of the most influential lifestyle factors are smoking and obesity.
- Smoking: Smoking has been strongly linked to HS. The chemicals in cigarettes can trigger and exacerbate inflammation throughout the body, including the skin. Smoking is known to impair immune function and wound healing, which can worsen HS symptoms and hinder recovery.
- Stress: Emotional and physical stress can trigger HS flare-ups. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, therapy, and a balanced lifestyle can help control symptoms.
- Diet: While research is ongoing, some studies suggest that certain foods may trigger HS flare-ups. A diet low in dairy and sugar has been reported to help some individuals manage their symptoms.
- Environmental Factors: Heat and humidity can exacerbate HS symptoms by increasing sweating and skin friction. Keeping cool and wearing breathable clothing can help minimize discomfort.
Understanding these causes can help individuals with HS manage their condition more effectively. While there is no cure for HS, recognizing and addressing these contributing factors can significantly improve quality of life and reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Symptoms of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
HS presents with various symptoms that can range in severity:
- Painful Bumps: Small, painful lumps that resemble boils.
- Abscesses: These can break open and leak pus, leading to unpleasant odors.
- Scarring: Chronic HS can lead to scar formation and thickened skin.
- Sinus Tracts: Tunnels form under the skin connecting abscesses, which can become infected and further complicate the condition.
Stages of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
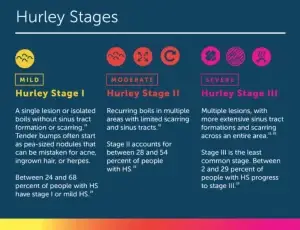
HS is often categorized into three stages based on severity:
- Stage 1: Single or multiple abscesses without sinus tracts or scarring.
- Stage 2: Recurrent abscesses with sinus tracts and scarring, often widely separated.
- Stage 3: Multiple interconnected sinus tracts and abscesses across an entire area of the body.
Diagnosing Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Diagnosing Hidradenitis Suppurativa can be challenging and often requires a thorough evaluation by a dermatologist. The diagnosis is primarily based on the characteristic symptoms and physical examination of the affected areas. In some cases, a biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions with similar symptoms such as folliculitis or abscesses. In addition to the physical examination, the healthcare provider may inquire about your medical history, including any family history of HS or similar skin conditions. Understanding the patient’s medical background, previous treatments, and the impact of the condition on the patient’s life is essential for accurately diagnosing and effectively managing HS.
It is very important to emphasize the need for early and accurate diagnosis of HS to initiate appropriate treatment and prevent potential complications. As HS is a chronic and progressive condition, timely intervention and ongoing management are crucial for improving quality of life and minimizing the long-term impact of the disease.
Treatment Options for Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Managing HS often requires a multifaceted approach, combining medications, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgical interventions:
- Medications:
- Antibiotics: Used to treat and prevent secondary bacterial infections.
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs: Help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Hormonal Therapy: Can be effective, particularly in women.
- Biologics: Target specific components of the immune system to reduce inflammation.
- Surgery:
- Incision and Drainage: Provides temporary relief for painful abscesses.
- Excision: Removal of affected skin areas to prevent recurrence.
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatments can reduce hair growth and inflammation.
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the severity of HS.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is essential as it worsens HS symptoms.
- Clothing: Wearing loose-fitting clothes to minimize friction and irritation.
Managing Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Living with HS requires ongoing management to reduce symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Skincare Routine: Gentle cleansing and avoiding harsh soaps can reduce irritation and prevent secondary infections.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers and warm compresses can alleviate discomfort.
- Diet: Some studies suggest that a diet low in dairy and sugar may help reduce HS flare-ups.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate HS, so techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and therapy can be beneficial.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have HS can provide emotional support and practical advice, helping individuals feel less isolated and more empowered to manage their condition.
Ongoing research aims to better understand the underlying causes of HS and to develop more effective treatments. Recent studies have focused on the genetic and immunological aspects of the disease, offering hope for more targeted therapies in the future. Clinical trials for new medications and treatment protocols are continually being conducted, and patients with HS may consider participating in these trials to access cutting-edge treatments. As we navigate the complexities of Hidradenitis Suppurativa, it is clear that while the journey is challenging, it is also one of hope and progress. Every step towards learning about HS, every treatment plan followed, and every lifestyle adjustment made represents an act of self-care and empowerment. By fostering a supportive community and leveraging the expertise of healthcare professionals, those living with HS are not alone. Ongoing evolution of research offers a beacon of light, working towards more effective therapies for HS on the horizon. By staying informed, connected and resilient, individuals with HS are not just coping; they are taking control of their health to move towards a future where HS is a condition managed, not a destiny defined.