With the abundance of sunscreen options available today, the task of selecting the right one can be overwhelming. A good sunscreen has a SPF of 30 or higher, provides broad-spectrum protection against both UVA and UVB rays, and is water-resistant. For sunscreen to remain effective, it is essential to reapply it every two hours, or more frequently if you are swimming or sweating heavily. The most effective sunscreen is the one that you will use consistently. Now, let us explore the diverse range of sunscreens available on the market today, sunscreen properties, and discuss how to choose the best option for your specific preferences and needs.
Sun protection factor (SPF)
SPF is a measure of how much UV radiation is required to cause sunburn. SPF measures how much longer it takes for UV radiation to cause a sunburn on skin protected with sunscreen compared to unprotected skin. For example, SPF 30 means it takes 30 times longer to cause a sunburn than if you were without sunscreen. SPF 30 blocks about 97% of UVB light, while SPF 50 blocks about 98% of UV lights. The higher the SPF, the better protection against UV light, however, no sunscreen blocks 100% of UV light. The American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) suggests using a sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
Chemical vs mineral sunscreens 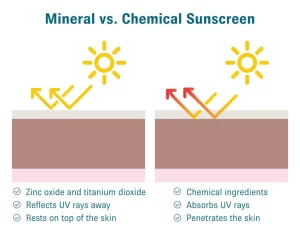
Mineral sunscreens, also known as organic or physical sunscreens, create a physical barrier on the skin that reflects UV light. They typically contain ingredients such as titanium dioxide or zinc oxide and have a thicker, opaque consistency. Mineral sunscreens provide immediate protection upon application.
On the other hand, chemical sunscreens contain active ingredients such as avobenzone, oxybenzone, and octisalate. These chemicals absorb UV light, thereby preventing skin damage. Chemical sunscreens are usually more sheer compared to mineral ones and require about 15 minutes to become effective after application.
There are also hybrid sunscreens that combine ingredients from both chemical and mineral sunscreens. All three types of sunscreens—mineral, chemical, and hybrid—are effective in protecting the skin against UV damage.
How much sunscreen do I need to apply?
Most adults require approximately one ounce of sunscreen to adequately cover their entire body. Sunscreen should be applied to all exposed areas of the body that are not covered by protective clothing. It is also important to apply sunscreen to the back of the feet and hands, neck, ears and head. Additionally, the lips are susceptible to sun damage and require protection as well; using lip balms with SPF 30 or higher is recommended to safeguard against UV exposure. With reapplication, a family of four should anticipate using about one four-ounce bottle of sunscreen per person for a full day spent outdoors.
What is a broad-spectrum sunscreen?
There are two types of harmful UV rays: UVA and UVB. UVA (aging rays) rays contribute to skin aging, casing wrinkles and age spots. They can also pass through standard window glass. UVB (burning rays) cause sunburn and are linked to skin cancer. They are normally blocked by window glass. A broad-spectrum sunscreen protects against both UVA and UVB rays. Skin Cancer Foundation and AAD recommend using broad-spectrum sunscreen for comprehensive protection against UV damage.
How frequently should sunscreen be reapplied?
For effective protection against the sun’s harmful effects on the skin, sunscreen should be reapplied approximately every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating heavily. When it comes to reapplying sunscreen, there are different formulations available to suit various needs. Powder sunscreen stands out as a particularly convenient choice for reapplication on the face. It is effortless to apply and blends smoothly over makeup, ensuring effective protection throughout the day.
What is water-resistant sunscreen?
Water-resistant sunscreen indicates how long the sunscreen remains effective on wet skin. Typically, most sunscreens are water-resistant for about an hour. No sunscreen is water – or sweatproof. Therefore, it is important to reapply sunscreen after swimming or sweating heavily. Always check the sunscreen label for specific details on its water resistance duration.
Sunscreens have an expiration day
The FDA mandates that sunscreens remain effective for up to 3 years, but not all sunscreens reach this duration. It is important to check the expiration date on your sunscreen to ensure proper sun protection. Expired sunscreens may lose effectiveness and should not be used. Always discard and replace expired sunscreen to maintain adequate protection against UV rays.
Different sunscreen formulations
Sunscreens are available in various forms such as cream, lotion, spray, stick, powder, gel, tinted, and clear formulations. Additionally, there are skincare and makeup products that incorporate SPF. Creams are ideal for dry skin and facial application. Gels are preferred for oily or hairy skin types. Sprays are convenient but require thorough application and rubbing to ensure effective sun protection. Tinted sunscreens not only protect against UVA and UVB rays but also offer additional protection against visible light. Including SPF in skincare and makeup products provides added benefits for sun protection.
What about babies? 
AAD advises against applying sunscreen to babies under 6 months old. The most effective way to protect infants in this age group is to keep them out of direct sunlight entirely. Dressing them in lightweight clothing and ensuring they remain in shaded areas outdoors is essential. If avoiding sunlight is not possible, a mineral-based, water-resistant sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher can be gently applied to exposed skin, ensuring it is washed off when indoors.
Sunscreen use should be supplemented by other sun-protective measures
In addition to applying sunscreen daily, it is essential to wear wide-brim hats, sunglasses, and long-sleeve protective clothing. Seeking shade whenever possible is crucial, particularly during the hours from 11 am to 3 pm when the sun is most intense and can lead to sunburn. These precautions help minimize exposure to harmful UV rays and reduce the risk of skin damage.
Sunscreen choices depend on personal preference. The best sunscreen is the one that a person will use consistently. Sunscreen should be broad-spectrum, with SPF 30 or higher, and water-resistant. Proper sunscreen application includes daily application of 1 once of sunscreen on the entire body surface area and reapplication every 2 hours, or sooner, if swimming or sweating profusely. Different sunscreen formulations cater to specific needs; for instance, tinted sunscreens not only protect against UVA and UVB rays but also offer additional defense against visible light. Comprehensive sun protection involves all of the above!