Join 1000s Who Trust DermOnDemand
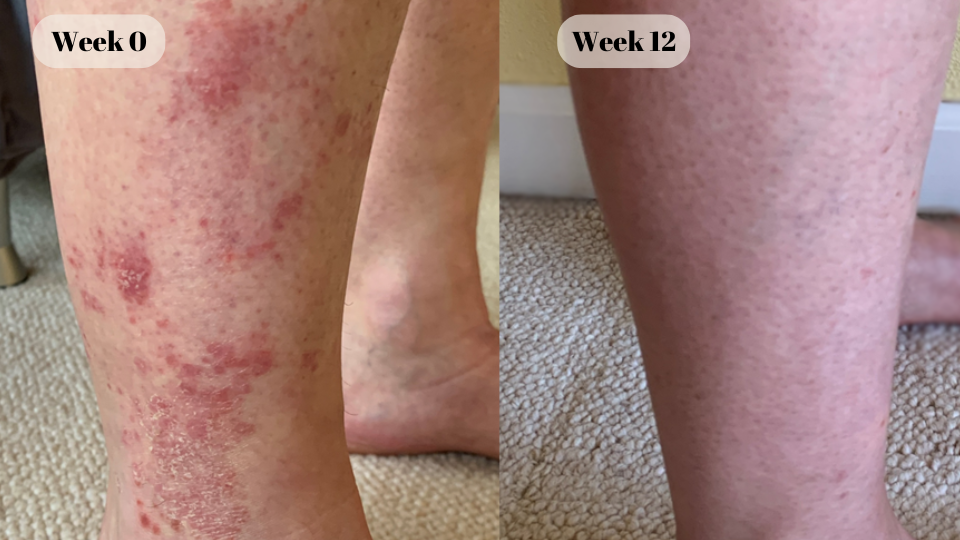
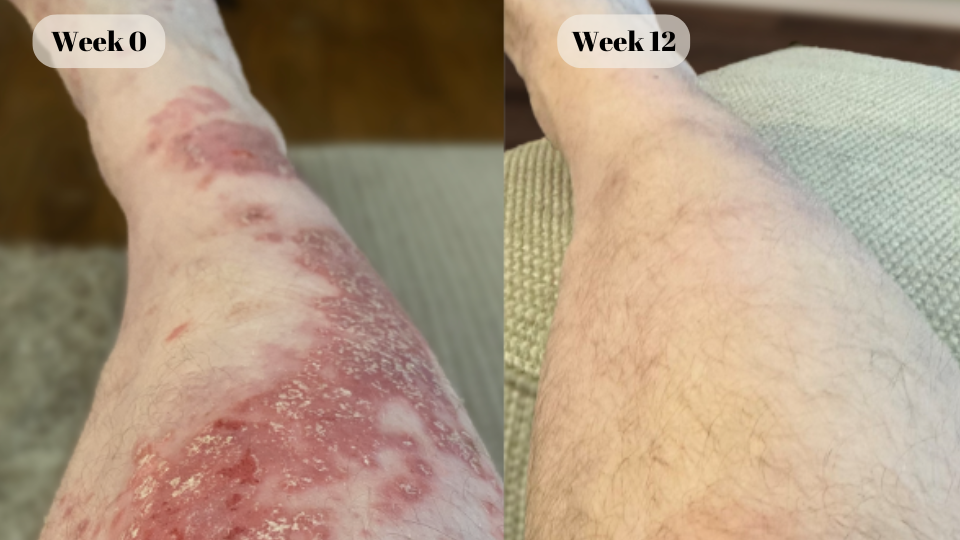
“Very happy to have been able to clear my skin conveniently from home.”
Samuel
DermOnDemand patient
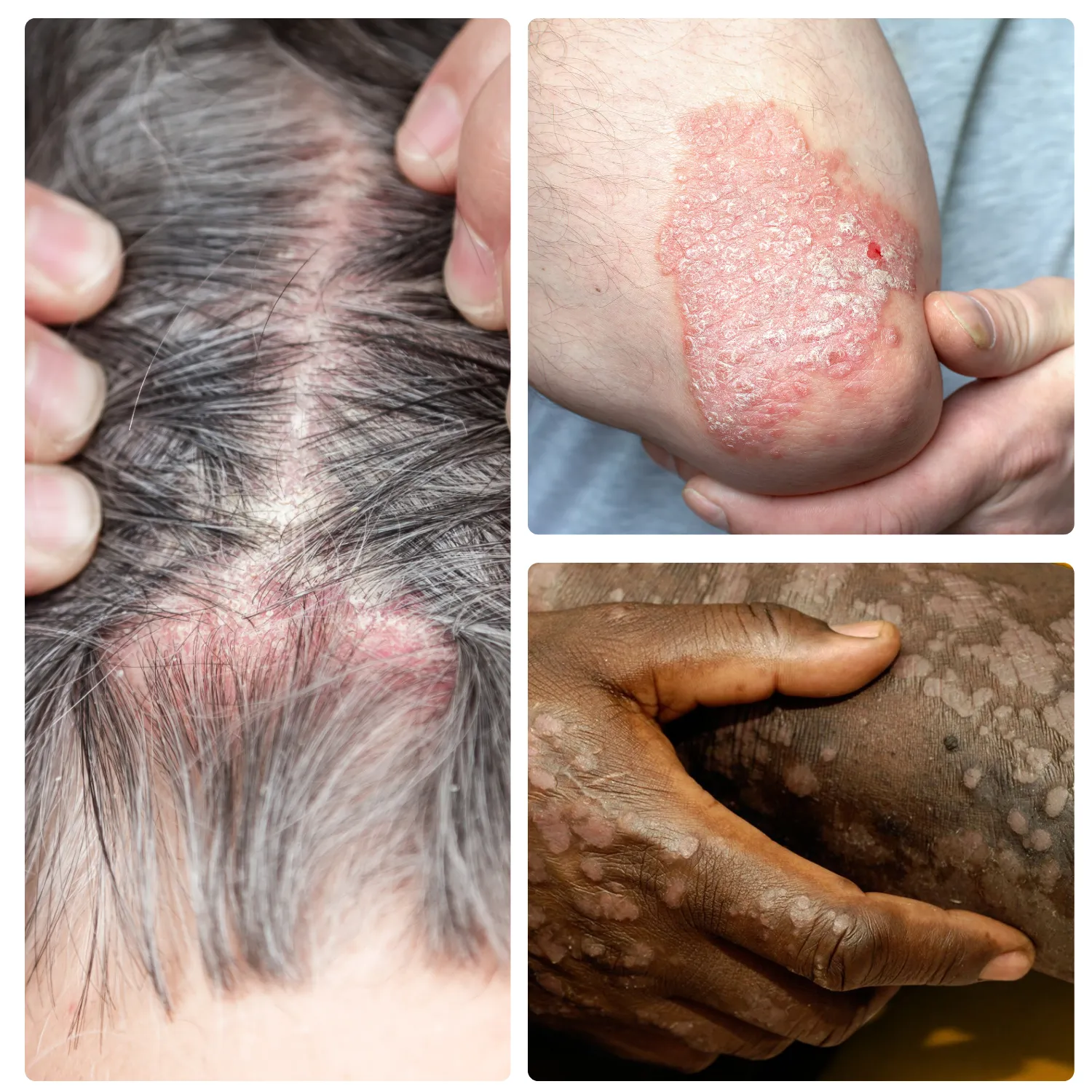
“My cystic acne had been bothering me for a while, but now it's gone so thank you!”
Katie
DermOnDemand patient
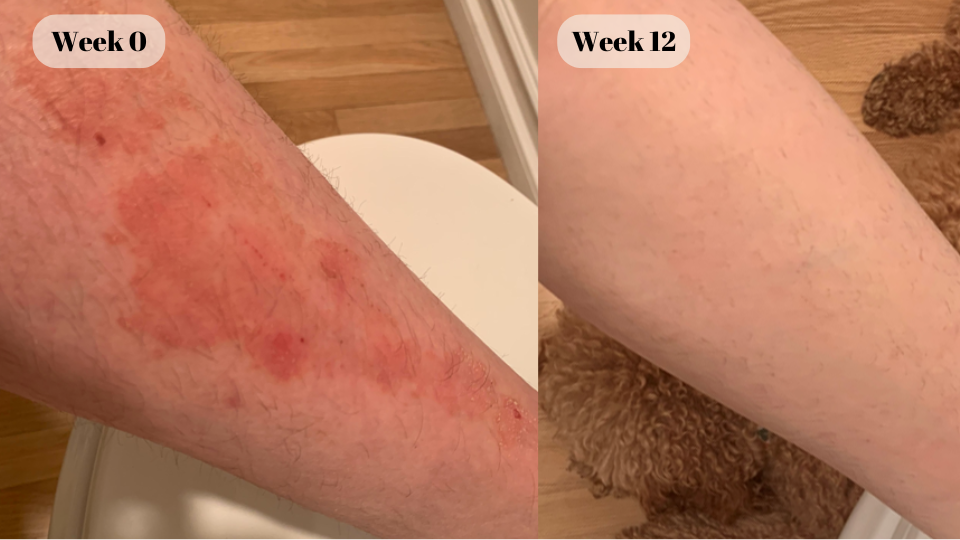
“Acne annoyed me much of my life because of the constant visits to the dermatologist, now I can be treated from home.”
Talia
DermOnDemand patient
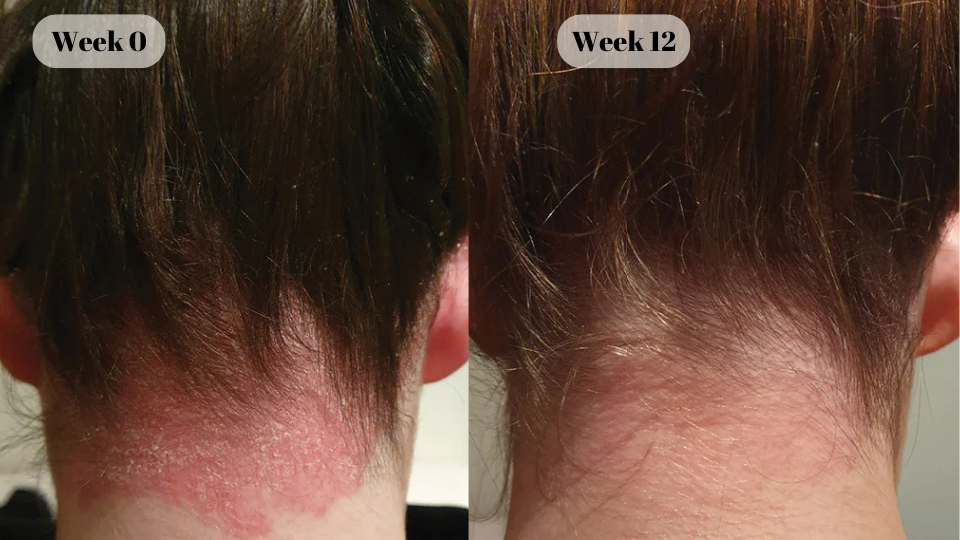
“DermOnDemand thank for making this possible to get great care for my acne without having to take off from work.”
Holly
DermOnDemand patient
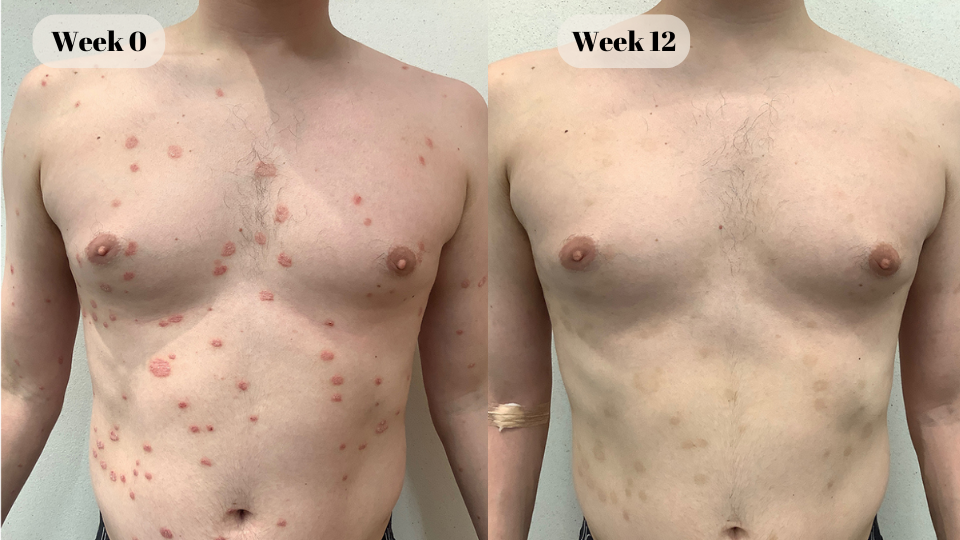
“Feeling blessed with my clear skin that I finally achieved.”
Riley
DermOnDemand patient
Quickly share your skin concerns by answering a few questions and uploading photos—it takes just 5 minutes.

Our dermatology team will carefully review your information, diagnose your condition, and create a tailored plan within 24 hours.
Your customized plan will be sent directly to you, and prescriptions (if needed) will go straight to your pharmacy.